Why Your Jupyter Notebook Won’t Display on GitHub (And How to Fix It)
If you have ever tried to upload a Jupyter notebook to GitHub only to see an “Invalid Notebook” error or no output showing up, you are not alone. This blog will help you understand why this happens and show you simple ways to fix it.
📘 You can explore the related notebook here: Widget Cleanup Notebook
This post is part of the Generative AI Lab, a public repository that explores creative and practical uses of LLMs, Vision-Language Models (VLMs), and multimodal AI pipelines. If you are curious about how these systems can be chained together to automate creative workflows, feel free to explore the other blogs in the repository to discover more exciting applications.
📚 Table of Contents
- 🚨 The Problem: Progress Bars Break GitHub Notebook Rendering
- ❓ Why This Happens
- 🛠️ How to Fix It
- 🎬 Outro
🚨 The Problem: Progress Bars Break GitHub Notebook Rendering
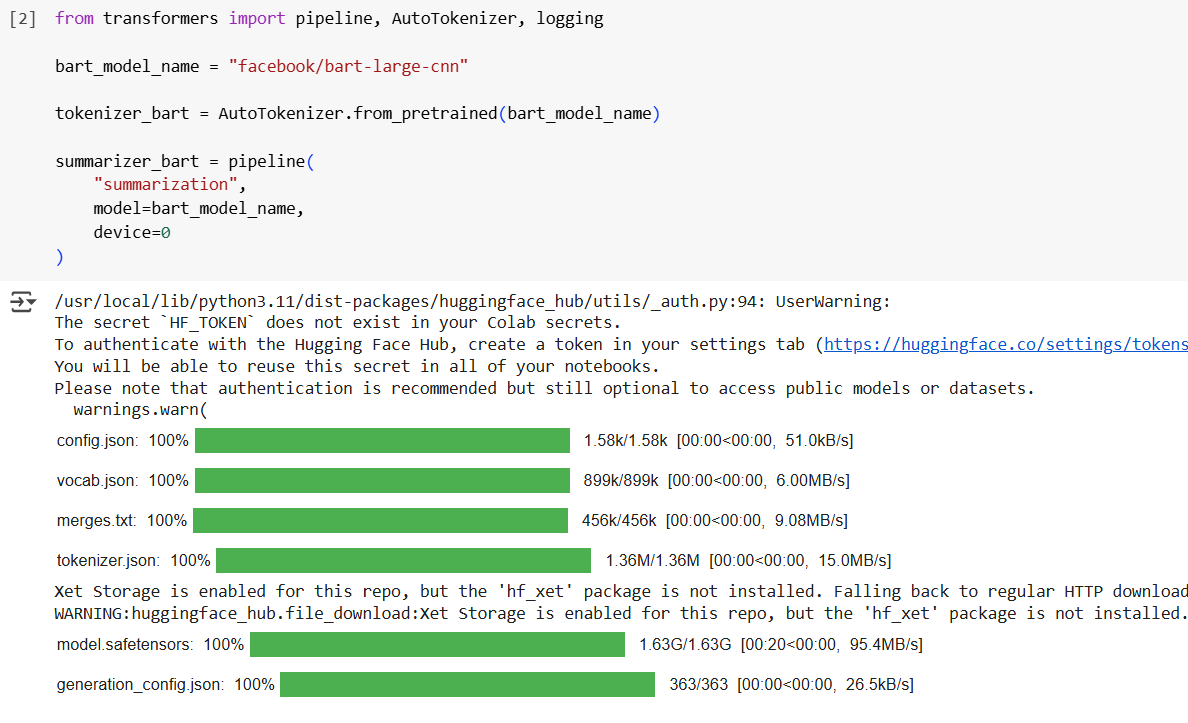
When you run long tasks in notebooks—like downloading large models or datasets—you often see progress bars that keep you informed. Popular libraries like Hugging Face’s Transformers use tqdm-based progress bars for this.
However, these progress bars create interactive widget metadata inside the notebook’s JSON, which GitHub tries to render. If this metadata is incomplete or corrupted, GitHub throws errors such as:
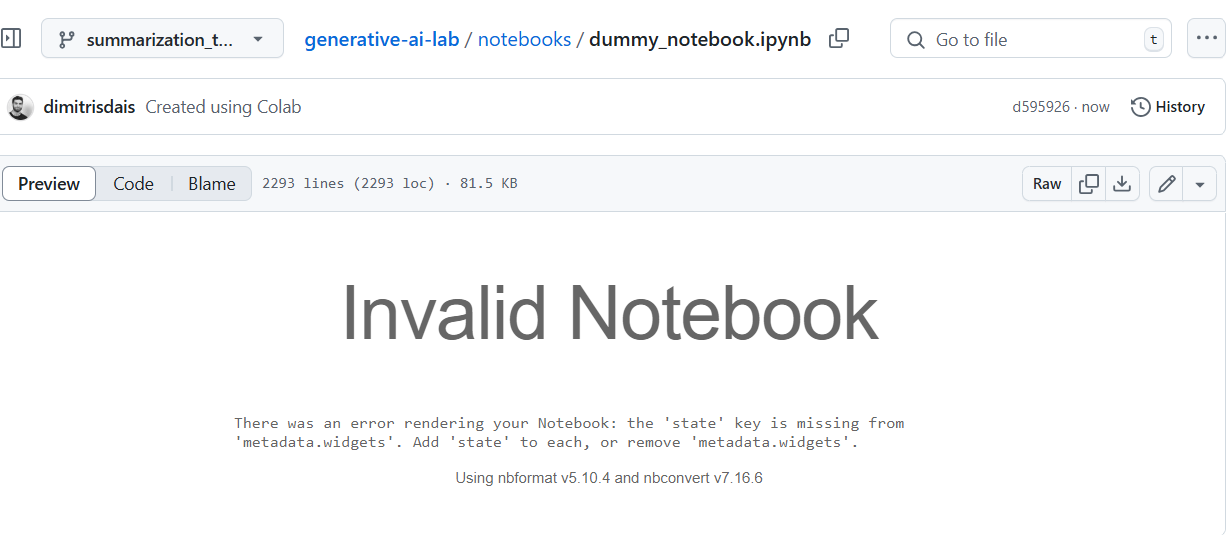
Invalid Notebook
There was an error rendering your Notebook: the ‘state’ key is missing from ‘metadata.widgets’. Add ‘state’ to each, or remove ‘metadata.widgets’.
This means GitHub cannot display your notebook preview properly as shown below.
❓ Why This Happens
The widget metadata (in the notebook JSON) contains information needed to render interactive elements. When you run progress bars or ipywidgets, this metadata is created. If you manually edit or upload a notebook with incomplete or broken widget metadata, GitHub refuses to render it.
One common example is loading a Hugging Face summarization model in Google Colab:
🛠️ How to Fix It
1. Clear All Outputs Before Uploading
This is the simplest but harshest option. You clear all outputs (progress bars, results) before saving and uploading. This ensures no widget metadata is saved, so GitHub can render the notebook.
Downside: No outputs mean users can’t see any progress or results inline, reducing the notebook’s usefulness.
2. Clean Widget Metadata Programmatically After Running
You can keep your outputs but remove the problematic widget metadata using a cleanup script.
For example, this Python snippet loads your notebook JSON, deletes all “widgets” entries from metadata (both cell-level and notebook-level), and saves a cleaned notebook:
import json
with open('notebook_with_widgets.ipynb', 'r') as f:
notebook = json.load(f)
if 'widgets' in notebook.get('metadata', {}):
del notebook['metadata']['widgets']
for cell in notebook.get('cells', []):
if 'widgets' in cell.get('metadata', {}):
del cell['metadata']['widgets']
with open('notebook_cleaned.ipynb', 'w') as f:
json.dump(notebook, f, indent=2)
This removes progress bars but keeps textual output and warnings.
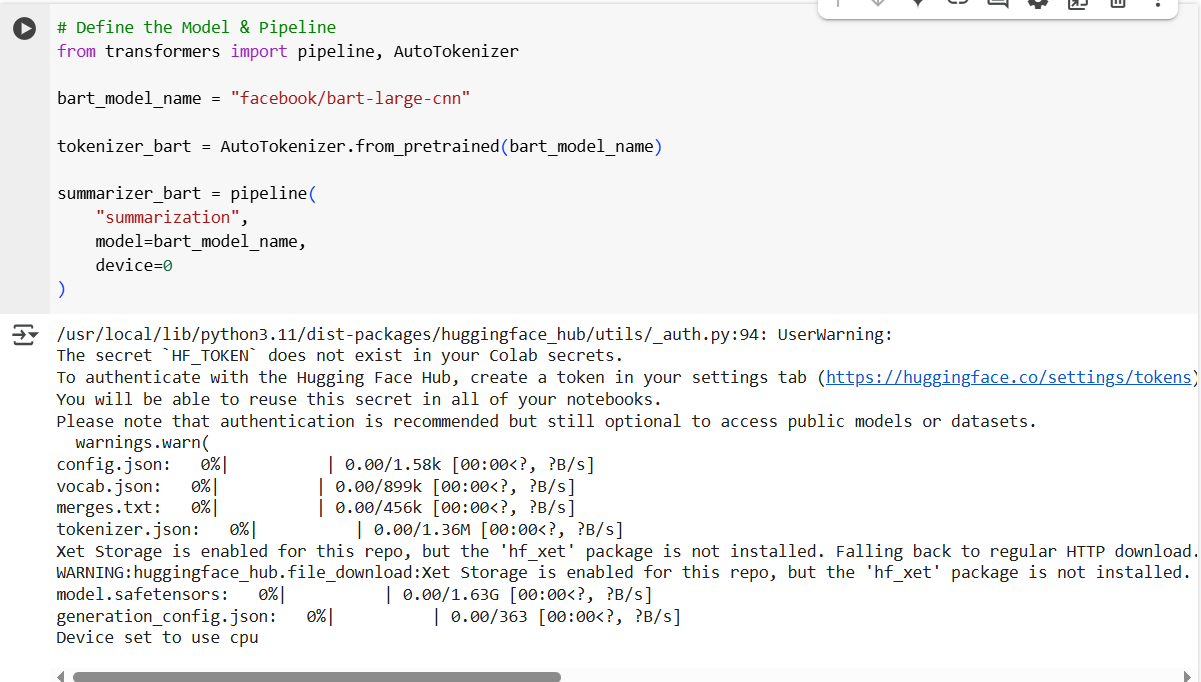
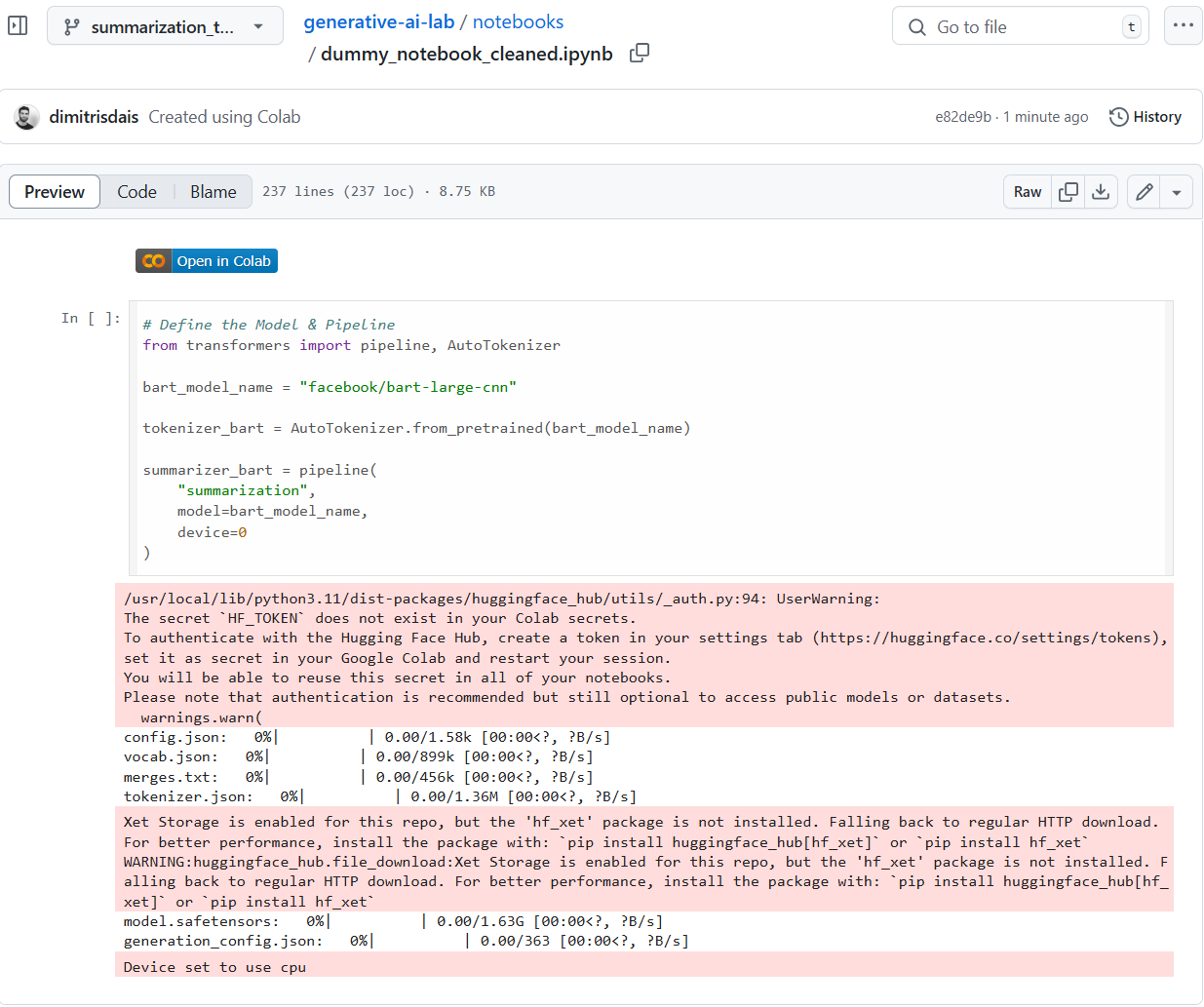
3. Disable Progress Bars When Running the Notebook
You can disable progress bars programmatically when loading models or pipelines, preventing the creation of widget metadata in the first place.
For example, when defining the Hugging Face pipeline, use the progress_bar argument set to False:
# Define the Model & Pipeline
from transformers import pipeline, AutoTokenizer
bart_model_name = "facebook/bart-large-cnn"
tokenizer_bart = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(bart_model_name)
summarizer_bart = pipeline(
"summarization",
model=bart_model_name,
device=0,
**{"progress_bar": False}
)
This disables the progress bars and helps avoid rendering issues on GitHub.
🎬 Outro
Thanks for reading — I hope you found it useful and insightful.
Feel free to share feedback, connect, or explore more projects in the Generative AI Lab.
